Classification of Volcano Eruption Status using Template Matching Analysis and the K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55732/jikdiskomvis.v8i2.1061Keywords:
Volcanic eruptions, seismograph image classification, machine learning, template matching, K-Nearest NeighborsAbstract
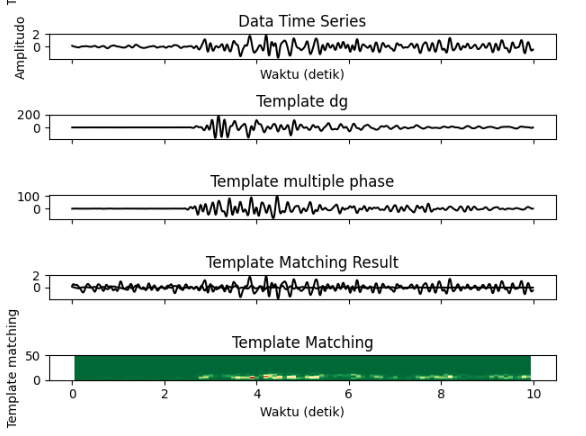
One type of natural disaster that occurs in Indonesia is a volcanic eruption. This is because Indonesia has hundreds of active volcanoes with different types of eruptions and status for each volcano, Indonesia is a country that is considered to be the island with the largest number of active volcanoes in the world. Even though seismographs are used to record volcanic activity, these tools can still not classify the type of earthquake and the status of volcanic eruptions. To overcome this, researchers propose using Machine Learning to classify volcanic eruption status. Machine Learning is a branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that facilitates human performance. There are seven branches of AI, including machine learning. In this research, Machine Learning methods were used as Template Matching and K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) to classify the type and status of volcanic eruptions. The test results are in the form of confusion matrix accuracy, recall, precision, and F1 score where to find the best K in the KNN model is divided into K=1, 3, 5, 7, 11. The results obtained are the best K at a data ratio of 90:10, namely K=1 where accuracy on big data (majority) is 91% and accuracy on all data (total data) is 87%. The test results also include how the KNN model predicts new data using KNN.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Computer Science and Visual Communication Design

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.






